Acilog SC Injection 100IU/ml (3ml Vial) 1's pack

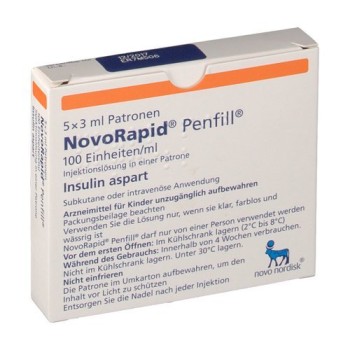

Acilog SC Injection 100IU/ml (3ml Vial) 1's pack
৳ 450.00/=
Ex Tax: ৳ 450.00/=
- Stock: In Stock
- Model: Medi-00029
- Generic: Insulin Aspart (rDNA)
- Pack Size: Each Pack contains 3ml Vial of Acilog Injection
0 items sold
7865 views
Available Options
Indications
Insulin Aspart is a rapid acting human insulin analog indicated to improve glycemic control in adults and children with diabetes mellitus.
Therapeutic Class
Rapid Acting Insulin
Pharmacology
The primary activity of Insulin Aspart is the regulation of glucose metabolism. Insulin Aspart bind to the insulin receptors on muscle and fat cells and lower blood glucose by facilitating the cellular uptake of glucose and simultaneously inhibiting the output of glucose from the liver.
Dosage
Usual range: 0.5-1 units/kg/day. When used in a meal-related SC inj treatment regimen, insulin aspart may provide 50-70% of total insulin requirement with the remainder provided by an intermediate-acting or long-acting insulin
The dosage of insulin aspart must be individualized
Subcutaneous injection: insulin aspart should generally be given immediately (within 5-10 minutes) prior to the start of a meal
Use in pumps: Change the insulin aspart in the reservoir at least every 6 days, change the infusion set, and the infusion set insertion site at least every 3 days
insulin aspart should not be mixed with other insulins or with a diluent when it is used in the pump
Intravenous use: Insulin aspart should be used at concentrations from 0.05 U/mL to 1.0 U/mL insulin aspart in infusion systems using polypropylene infusion bags. insulin aspart has been shown to be stable in infusion fluids such as 0.9% sodium chloride
The dosage of insulin aspart must be individualized
Subcutaneous injection: insulin aspart should generally be given immediately (within 5-10 minutes) prior to the start of a meal
Use in pumps: Change the insulin aspart in the reservoir at least every 6 days, change the infusion set, and the infusion set insertion site at least every 3 days
insulin aspart should not be mixed with other insulins or with a diluent when it is used in the pump
Intravenous use: Insulin aspart should be used at concentrations from 0.05 U/mL to 1.0 U/mL insulin aspart in infusion systems using polypropylene infusion bags. insulin aspart has been shown to be stable in infusion fluids such as 0.9% sodium chloride
Administration
Administer 5-10 min before meal
Interaction
Effects may be increased by: oral antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, MAOIs, propoxyphene, salicylates, somatostatin analog (e.g., octreotide), sulfonamide antibiotics. Effects may be decreased by: corticosteroids, niacin, danazol, diuretics, sympathomimetic agents, isoniazid, phenothiazine derivatives, somatropin, thyroid hormones, oral contraceptives, lithium. Signs of hypoglycaemia may be masked by β-blockers, clonidine.
Contraindications
Insulin Insulin Aspart is contraindicated-
- during episodes of hypoglycemia
- in patients with hypersensitivity to Insulin Aspart or one of its excipients
Side Effects
Hypoglycaemia; oedema; pruritus; rash; hypersensitivity reactions; lipoatrophy or lipohypertrophy with SC Inj (rotate Inj site).
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Category B. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcome regardless of drug exposure. This background risk is increased in pregnancies complicated by hyperglycemia and may be decreased with good metabolic control. It is essential for patients with diabetes or history of gestational diabetes to maintain good metabolic control before conception and throughout pregnancy. Insulin requirements may decrease during the first trimester, generally increase during the second and third trimesters, and rapidly decline after delivery. Careful monitoring of glucose control is essential in these patients. Therefore, female patients should be advised to tell their physician if they intend to become, or if they become pregnant while taking insulin aspart.
Precautions
Renal or hepatic impairment; pregnancy; lactation. Transferring from other insulin. Monitor serum glucose, potassium, electrolytes, HbA1c and lipid profile. Concomitant illness esp infections; hypokalaemia.
Use in Special Population
Renal Impairment: Decreased dose may be necessary.
Hepatic Impairment: Decreased dose may be necessary.
Hepatic Impairment: Decreased dose may be necessary.
Source: medex.com.bd